Uncovering The Truth About Bipolar Disorder: Must Read
Bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic depression, is a complex mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). Despite its prevalence and impact on individuals and society, bipolar disorder remains widely misunderstood. This article aims to delve into the depths of bipolar disorder, uncovering its truths, dispelling myths, and shedding light on its diagnosis, treatment, and everyday realities.
https://www.youtube.com/@akhildhanda8867
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
At its core, bipolar disorder disrupts the brain’s normal functioning, affecting mood, energy levels, and the ability to carry out day-to-day tasks. Contrary to common misconceptions, bipolar disorder is not simply moodiness or occasional shifts in temperament. It is a serious mental illness that requires proper diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is not a one-size-fits-all condition. It exists along a spectrum, with different types and variations. The primary types include:
Bipolar I Disorder: Characterized by manic episodes that last at least seven days or by manic symptoms that are so severe that immediate medical care is necessary. Depressive episodes typically occur as well, lasting at least two weeks.
Bipolar II Disorder: consists of a cycle of hypomanic and depressed episodes rather than the full-blown manic episodes found in Bipolar I.
Cyclothymic Disorder (Cyclothymia): A milder form of bipolar disorder characterized by periods of hypomanic symptoms as well as periods of depressive symptoms lasting for at least two years (one year in children and adolescents).
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of bipolar disorder is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurobiological factors. Family history plays a significant role, with individuals having a close relative with bipolar disorder being at a higher risk. Stressful life events, substance abuse, and changes in sleep patterns can also trigger or exacerbate symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms and Diagnostic Criteria
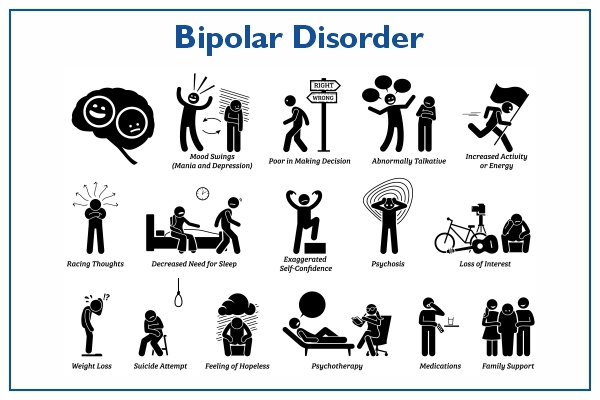
Understanding the signs and symptoms of bipolar illness is essential for a precise diagnosis and prompt treatment. Symptoms of mania or hypomania may include:
- Increased energy and activity levels
- Elevated mood or irritability
- Racing thoughts and impulsivity
- Decreased need for sleep
- Grandiose beliefs or unrealistic optimism
- Poor judgment and risky behavior
Depressive symptoms may include
- Persistent sadness or hopelessness
- Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Fatigue or low-energy
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and assessment of symptoms. Mental health professionals may also utilize standardized diagnostic criteria, such as those outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for bipolar disorder often involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle modifications. Mood stabilizers, such as lithium and anticonvulsants, are commonly prescribed to manage mood swings and prevent relapse. Antidepressants and antipsychotic medications may also be used in certain cases, but caution is needed to avoid triggering manic episodes.
Psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy, can help individuals develop coping skills, improve mood regulation, and address underlying issues contributing to their symptoms. Lifestyle factors, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and recreational drugs, can also play a significant role in managing bipolar disorder.
Challenges and Realities
Living with bipolar disorder can present numerous challenges, both for individuals diagnosed with the condition and their loved ones. Stigma and misconceptions surrounding mental illness can lead to feelings of shame, isolation, and reluctance to seek help. Managing medications, coping with mood swings, and navigating interpersonal relationships can also be daunting tasks.
However, if they receive the proper support and care, many people with bipolar disorder can lead happy and fulfilling lives. It is essential for individuals to work closely with mental health professionals, develop a support network, and prioritize self-care to effectively manage their condition.
Conclusion
Worldwide, bipolar disorder affects millions of people and is a complex, occasionally misdiagnosed mental illness. By gaining a deeper understanding of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we can work towards reducing stigma, increasing awareness, and improving outcomes for those living with bipolar disorder. With early intervention, comprehensive treatment, and ongoing support, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead meaningful and fulfilling lives, free from the constraints of their condition.
For any further queries, Plz visit psychiatristdrakhildhanda.com or you can check our social media accounts, Facebook, Instagram